Introduction
PyEPlan is an open-source Py-thon-based E-nergy Plan-ning tool for design and operation of optimized microgrid networks. It supports functions ranging from renewable generation profile creation, network layout design to optimization of design and operation costs for microgrids packaged in three main modules. Used independently and/or jointly, the different packages provide the user with detailed analysis of short and long-term costs and benefits of different generation resources and impacts of their characteristics on system operation. The tool is customizable allowing users to neglect or input desired network characteristics, choose from a pool of generation sources both renewable and non-renewable, etc.
PyEPlan addresses the growing need for sustainable energy solutions in developing regions and remote communities by providing a comprehensive framework for microgrid planning and operation. The tool incorporates advanced optimization techniques and machine learning algorithms to handle the inherent uncertainty in renewable energy generation and load demand patterns.
The initial development of the tool was funded under the UKRI GCRF project CRESUM-HYRES at the University of Leeds, but is now supported and co-developed by people in different universities (such as CUT, ICL).
In the next sections detailed information on functionality of each supported module, installation and usage is provided.
Functionality
The functions available in PyEPlan are packaged into three key modules that can be utilized independently or simultaneously:
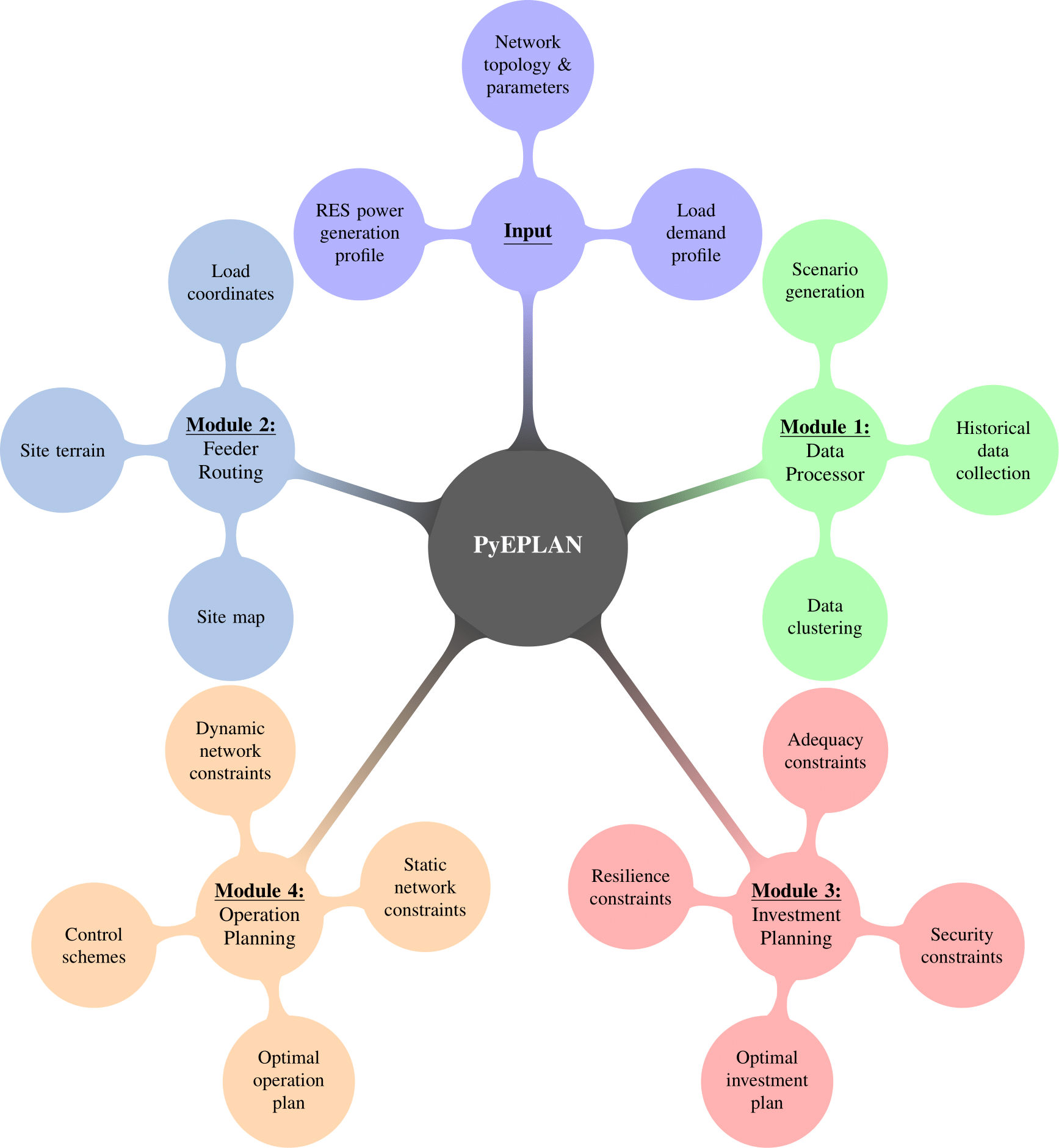
Data Processing System (datsys)
The Data Processing module supports two main functionalities:
Historical Data Extraction: It extracts historical data on wind speed and solar radiation based on user-provided coordinates of the generation source location from openly available satellite information and creates 24-hour daily profiles for the given period of time. This data is sourced from PVGIS (Photovoltaic Geographical Information System) API, which provides access to multiple radiation databases including SARAH2, ERA5, and NSRDB.
Representative Day Clustering: It finds representative days based on daily profiles of load demands and power generations of renewable energy sources by applying machine learning algorithms such as K-means clustering. The representative days are used as operation scenarios providing the input data needed for the investment/operation planning modules, significantly reducing computational complexity while maintaining solution accuracy.
Routing System (rousys)
The Routing module finds the least cost network design given the geographical distances between nodes, technical line parameters and cost of the different line types. It takes user map coordinates of the node or load point locations and provides an optimal system layout using the minimum spanning tree algorithm. The module considers:
Geographic Constraints: Real-world terrain and accessibility factors using Haversine distance calculations
Technical Parameters: Line resistance, reactance, and current carrying capacity
Economic Factors: Capital costs for different cable types and installation
Network Topology: Radial network configurations using minimum spanning tree
Investment and Operation System (inosys)
This module combines both investment and operation planning in a unified optimization framework using mixed-integer linear programming (MILP). Capabilities include:
Optimal Technology Sizing: Determination of optimal capacity for renewable generators, energy storage, and conventional units
Optimal Siting: Geographic placement of generation and storage facilities
Cost Analysis: Capital and operation costs predictions with detailed financial modeling
Grid Integration: On-grid and off-grid modeling capabilities
Uncertainty Handling: Scenario-based optimization considering weather variability and load uncertainty
Real-time Dispatch: Optimal unit commitment and economic dispatch considering technical constraints
Battery Energy Storage: Comprehensive modeling of battery charging/discharging cycles and state of charge
The investment and operation planning module requires network characteristics (i.e., candidate/existing lines) as well as long-term/short-term estimated/forecasted load demands and power generations of RESs to obtain the optimal solution. The former can be user defined or obtained from the Routing module, and the latter can be user defined or obtained from the Data Processing module.
Since the investment and operation planning module includes various optimization problems, the open-source, Python-based, optimization modeling module Pyomo is used with diverse abilities in formulating, solving, and analyzing optimization problems. Additionally, PyEPlan can utilise a broad range of solvers both open-source and commercial as supported by Pyomo, to obtain the optimal solution in both investment and operation planning modules.
What PyEPlan uses under the hood
PyEPlan is built on a robust foundation of scientific Python packages:
pandas for data manipulation and time series analysis
numpy and scipy for numerical computations and optimization algorithms
pyomo for mathematical optimization modeling and problem formulation
matplotlib for data visualization and plotting
networkx for graph algorithms and network analysis
scikit-learn for machine learning and clustering algorithms
openpyxl for Excel file handling
timezonefinder for geographic timezone calculations
urllib for API communication with PVGIS
Other comparable software
HOMER Energy
RETScreen
Target user group
PyEPlan is a tool intended for researchers, planners and students aiming at the creation and operation of cost-optimised resilient and sustainable microgrid networks.
Licence
PyEPlan is released under the Apache License 2.0.